Binary Search
版权声明:本文为 DLonng 原创文章,可以随意转载,但必须在明确位置注明出处!
Binary Search is a basic search algorithm. Its basic idea is each search is reduced by half of the data. Such as,using Binary Search to search 2 in this table :
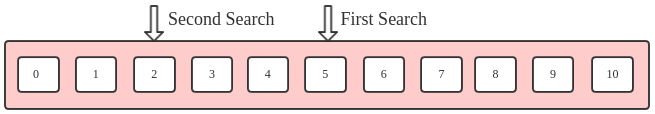
1. First search index = (0 + 10) / 2 = 5,and 2 < 5,then search [0, 4]
2. Second search index = (0 + 4) / 2 = 2, and 2 == 2,find it !
Before you use Binary Search,you must be know below points :
1. Binary Search O(n) = O(log2n)
2. The set of searchs it must be ordered(Ascending or Descneding),such as above array table.
3. It applies to infrequently changing and finding frequent ordered lists.
Now,we see the algorithm code.
Algorithm Code
I use C to coding,like below :
Array and division
Using arrays and division is the easiest way :
int *binary_search_common(int *array, int length, int key) {
int low = 0;
int mid = 0;
int high = length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
mid = (high + low) / 2;
printf("binary_search_common: mid = %d\n", mid);
if (key < array[mid])
high = mid - 1;
else if (key > array[mid])
low = mid + 1;
else
return array + mid; // Ok,find it !
}
// No find !
return NULL;
}
Point and right shift
Using pointer and right shift instead of array and division to improve efficiency :
int *binary_search_improve(int *array, int length, int key) {
int *low = array;
int *mid = NULL;
int *high = array + length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1);
printf("binary_search_improve: mid = %d\n", mid - low);
if (key < *mid)
high = mid - 1;
else if (key > *mid)
low = mid + 1;
else
return mid; // Ok,find it !
}
// No find !
return NULL;
}
Recursive
I suggest you`d better use recursion to achieve it again :
int *binary_search_rec(int *array, int *low, int *high, int key) {
if (low > high)
return NULL; // No find !
int *mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1);
printf("binary_search_rec: mid = %d\n", mid - low);
if (key < *mid)
return binary_search_rec(array, low, mid - 1, key);
else if (key > *mid)
return binary_search_rec(array, mid + 1, high, key);
else
return mid; // Ok,find it !
}
TestCode
I use an order array as test data :
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: ./a.out search_num:[0, 10]\n");
exit(1);
}
int a[11] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
int key = atoi(argv[1]);
int *find1 = binary_search_common(a, 11, key);
int *find2 = binary_search_improve(a, 11, key);
int *find3 = binary_search_rec(a, a, a + 11, key);
printf("%d\n", *find1);
printf("%d\n", *find2);
printf("%d\n", *find3);
return 0;
}
Compile and run :
gcc binary_search.c
./a.out 2
binary_search_common: mid = 5
binary_search_common: mid = 2
binary_search_improve: mid = 5
binary_search_improve: mid = 2
binary_search_rec: mid = 5
binary_search_rec: mid = 2
2
2
2
Can be seen,we only need to find 2 times. But,for an ordered list,it is not the fastest algorithm. For example,finding 2 still takes 2 times,but actually we can find 2 only once !
Continue to see the faster algorithm below !
Interpolation Search
Interpolation Search and Binary Search basically the same,the only difference is how to calculate mid.
In Binary Search :
mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1);
But in Interpolation Search :
mid = low + (high - low) * ((double)(key - array[low]) / (array[high] - array[low]));
What is it ? look below :
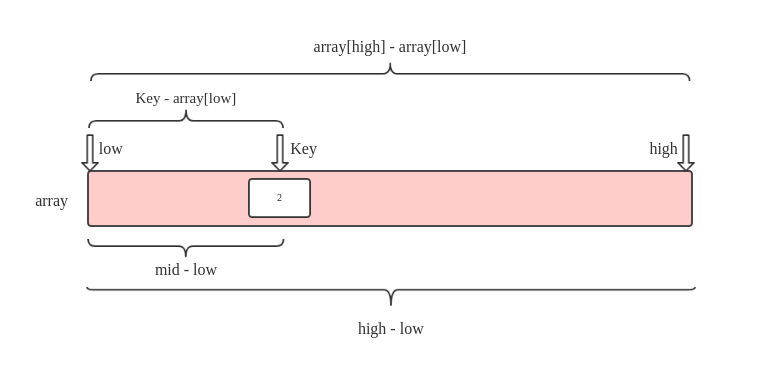
We calculate the mid by the following proportional formula :
(mid - low) / (high - low) = (key - array[low]) / (array[high] - array[low])
->
mid = low + (high - low) * (key - array[low]) / (array[high] - array[low]);
But we must be add double to case type,because we need to let 0 < (key - array[low]) / (array[high] - array[low]) < 1,if we do not case it to double,the expression will be zeor,so we must be case it to double :
// Case (key - array[low]) to double.
mid = low + (high - low) * ((double)(key - array[low]) / (array[high] - array[low]));
Point type,because point do not add to double,we need to case it to int so that it can add to point low :
mid = low + (int)((high - low) * ((double)(key - (*low)) / ((*high) - (*low))));
Interpolation Code
OK,now you only need to replace how to calculate the expression of mid can be achieved Interpolation Search :
int *binary_search_xxx(int *array, int length, int key) {
...
while (low <= high) {
// For array and division.
mid = low + (high - low) * ((double)(key - array[low]) / (array[high] - array[low]));
printf("binary_search_xxx: mid = %d\n", mid);
// For point and >>
mid = low + (int)((high - low) * ((double)(key - (*low)) / ((*high) - (*low))));
printf("binary_search_xxx: mid = %d\n", mid - low);
}
...
}
You can use the above code main function to test this algorithm,and the result like below :
gcc binary_search.c
./a.out 2
binary_search_common: mid = 2 // Note: We only need to search once !
binary_search_improve: mid = 2
binary_search_rec: mid = 2
2
2
2
This can be,thank you for reading.
DLonng at 06/13/17
